Focusing a camera and the first tests: Difference between revisions
RadimStano (talk | contribs) |
RadimStano (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Ahoj! In this section, cable the camera for the first time, do the preliminary focusing, configure your camera and optionally test the whole system. | Ahoj! In this section, cable the camera for the first time, do the preliminary focusing, configure your camera and optionally test the whole system. | ||
Revision as of 07:07, 18 October 2023
Ahoj! In this section, cable the camera for the first time, do the preliminary focusing, configure your camera and optionally test the whole system.
Testing and Focusing
At this point, your camera must be tested and focused. There's no point sealing up the housing and screwing it to the wall if its not working or isn't focused !
Testing the Camera
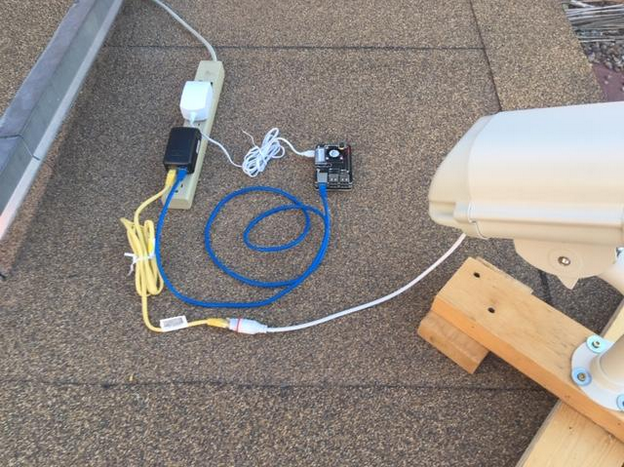
- If your camera came with a single PoE cable, connect this to a netork cable and plug the other end of the network cable into your PoE injector.
- if your camera came with a cable with separate network and power sockets, plug the "output" PoE adapter into the camera cable and plug a network cable into the PoE adapter, then connect the other end of the network cable into the other PoE adapter.
- . Connect the PoE adapter or injector into a spare socket on your home router and connect the camera power supply to it.
The Camera PoE cable lights should come on, indicating traffic is flowing. After a few seconds, it should steady down to irregular flashing. If you don't see flashing lights then check the cable connections to make sure everything is plugged in properly.
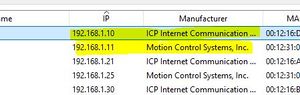
Find its IP AddressThe camera should now appear as a device on your network and to test it properly you will need to find its IP Address. The easiest way to do this is using a free piece of software called [IP Scanner]. Download and run it (no need to install). Click "Scan" and wait till it finishes. The camera can usually be identified by Manufacturer 'ICP Internet Communications' or 'Motion Control Systems', though other vendor names are possible such as 'Koenig & Bauer AG' and 'Metrohm AG'. If none of the names look right you may need to experiment by trying to connect to each candidate in turn. Checking the Connection
If the image is upside down in VLC, turn it through 180 degrees in the housing. do not be tempted to use firmware settings to flip or mirror the image. These cameras have a 'rolling' shutter and to work out precise timings of meteors, the RMS software compensates for the shutter movement. If the camera is upside down and the image then flipped, the shutter is working in the opposite direction to that expected by RMS and timings will be wrong. You must physically rotate the camera.
|
Checking for Obstructions of camera housingThis is to make sure that the camera housing is not too visible in the camera's FoV.
|
Focusing the CameraThere's a whole separate section of the Wiki on focusing, but here's the short version !!
You can usually do an initial focus with the camera assembled on a desk. Point it out a window during the hours of darkness and focus on a building at least 50m away. You can do this using the RMS utility ShowLivestream instead of VLC, if you have already fully configured the camera and Pi as explained in the next step. Note that there's a short lag due to the network, so you should wait a second or two after each adjustment to allow the change to be reflected in VLC. Important note: if your camera came with an electronic filter, and you have left the 'daytime' filter in place you MUST finalise focus at night. The filters slightly alter focus. |
[Optional] All system test
- Hook RPi up to a monitor with an HDMI cable
- Plug a keyboard and mouse into USB ports on the RPi
- Connect one end of an ethernet cable into the ethernet port on the RPi and the other end into the ‘LAN’ port on the POE injector (See image below).
- Connect another ethernet cable into the ‘POE’ port on the injector and run to the camera cable connector (See image below). Before plugging into the camera, run the cable end through the ethernet connector cover.
- Plug the POE injector into a wall outlet.
- Plug the RPi power supply into the RPi and then into a wall outlet.
- The first thing you would need to do is to connect it to WiFi. In the upper right corner, click on the two arrows pointing up and down, choose your WiFi network and enter the password. You should now be connected to the Internet.
- Ignore (for now) the steps in the terminal window shown on the screen which will help you set everything up.
- The video stream can be checked by double-clicking on the RMS.ShowLiveStream icon on the desktop. When asked, click ‘Execute in terminal’. You should then see a live stream from the camera. To stop the live stream hold down the ‘Ctrl’ key and press ‘c’ while the mouse is in the terminal window that popped up. Note that the stream will lag behind the real-view for a few seconds.
If the video stream opens and looks good, then you have successfully tested your system!
Camera setup & configuration
To operate at night, the camera must be reset to the correct gain, colour mode and video mode. There are two ways you can do this - doing it via the CMS software or via RMS scripts. In any case it is recommended to watch the below video.
Camera setup & configuration - Youtube video method
|
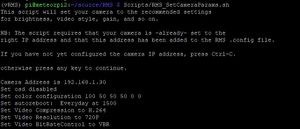
Camera setup & configuration - RMS Script methodNote that all RMS scripts MUST be run from the source/RMS folder as the Pi user. Don't be tempted to cd into a different folder! It won't work.
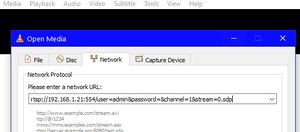
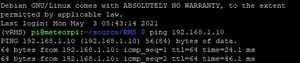
ping a.b.c.d If you get any errors or timeouts, check the camera IP address, and check that the Pi is connected to your home network.
python -m Utils.SetCameraAddress a.b.c.d 192.168.42.10
Scripts/RMS_SetCameraParams.sh
|
You are now done with this section and now you are going to install your camera into the position. Drilling holes into the wall is fun, right? Back to the signpost page.