Build A Camera
Parts and Tools needed
Click on the image to the right to see a larger version with the parts labelled
- IMX291 sensor board
- Lens with the lens holder - 4mm, 6mm are M16 mount as pictured, while other lenses might be CS which have a different holder
- 2x M2 screws
- Camera housing
- Small cable gland (supplied with the housing)
- Large cable gland (supplied with the housing)
- Camera Power over Ethernet (PoE) cable (sometimes called a network cable by the sellers)
- Camera board holder (supplied with the housing)
- Holder metal plate (supplied with the housing)
- 3x M2 screws, 12 mm long
- 1x M3-.50 screws, 6mm long
- Metal plate screws (supplied with the housing)
- Transparent weatherproof silicone
- Housing mounting bracket (supplied with the housing)
- Waterproof ethernet cable protector
- PoE injector to supply 48v to the camera (not shown)
- Raspberry Pi 4 Model B 2GB (or at least a 3B+ with 2GB) with official power supply (not shown)
- Raspberry Pi housing (not shown)
- 128 GB or greater microSD card (not shown)
- Self-amalgamating tape (not shown)
Purchasing Parts
For consistency across the network and to make collaborative support possible, it is recommended that the components listed below are used in preference to random handy bits that are cobbled together. The selected components are proven and known to work well.
Some components are readily available in most locations, such as Raspberry Pi and microSD cards. For all other items, AliExpress is the preferred online source as it serves most of the globe and has been reliably suppling parts to date.
Sensor
The following bare IP security camera featuring a Sony IMX291 has been selected for the RMS system. Out of the options offered, choose "With 48V POE cable" and "No Lens". The cost is typically less than US$45 plus shipping.
Lens
A suitable lens can be obtained for less than US$20 plus shipping. The preferred lens is a 4mm f/0.95 M16 lens providing ~88x45° field of view:
In very light-polluted city skies, an alternative is the 8mm f/0.9 M16 lens which provides ~40x20° field of view:
Some stations have also successfully utilized the following 6mm lens with a ~55x30° field of view:
Also on the approved lens list is the following 16mm f/1.0 lens that provides only a limited 20x10° field of view:
Note that this lens also requires a special CS lens mount, not supplied with the lens:
Housing
A security camera housing is used, providing weather-tight protection without distortion introduced by plastic domes. From the options offered, select "Plate and Bracket" to get a plate for mounting a 38x38mm bare IP camera module, and an L-shaped mounting bracket. The housing should be available for less than US$35 plus shipping.
- IP66 CCTV Camera Housing with Plate and Bracket This will also provide a pair of cable glands and some essential screws.
Power Over Ethernet Injector
This connects by network cables to both the Raspberry Pi and the camera sensor, and injects 48V DC onto the network cable to the camera to supply it with power. Pick a suitable plug style for your location from the options offered. This unit should be available for less than US$10 plus shipping.
Cooled Housing for Raspberry Pi
This is one of the rare cases that fulfills our needs. It has a fan which is relatively quiet, it’s sturdy, and it can fit the RTC with the addition of riser pins. Please buy this case, we have tried many others, but they are not as good. From the options offered, make sure you select one that says "for Pi 4" if you are using a Raspberry Pi 4, or "for Pi 3B Plus" if you are using a Raspbery Pi 3B+. Additionally there is a case variation that is fully enclosed and has no fans; do not select this option.
Real Time Clock for Raspberry Pi
As very precise timing is essential to processing the meteor data, an RTC module ensures the Raspberry Pi always has the precise time, even when power or internet is unreliable. AliExpress sells a pack of 10 but they are inexpensive - maybe share the extras among other camera constructors in your area. A pack of 10 should cost just over US$20 plus shipping.
Pin Headers
Required to raise the height of the Raspberry GPIO bins to allow the RTC to sit proud of the Raspberry Pi case. You only need 1 but the pack of 20 is available for less than US$1 plus shipping.
Network cabling
You will need two lengths of network cabling, one (probably quite short) between the Raspberry Pi and the PoE injector and the other between the PoE injector and the camera. You can purchase suitable lengths locally or on AliExpress. Some people have found the following thin flat network cable to be useful for sneaking the wire through a window or door to avoid drilling holes in walls or eaves, although it will require some extra attention to seal the cable at the camera's PoE connector:
Waterproof Cable Connector
One end of the network cable will be outside, connected into the PoE cable from the camera. This is not only carrying data but 48V DC power and needs to be kept sealed. This waterproof connector is fitted over the end of the network cable connector then after the network cable is plugged into the camera's PoE cable, the connector is locked into the end of the PoE cable. For extra weatherproofing, wrap in self-amalgamating tape. A pack of 10 waterproof connector caps is less than US$10 plus shipping.
128GB Micro SD Card
You need at least a 64GB card but a 128GB is recommended as 20+ GB of data is collected every night. Make sure it is a fast card eg Class 10 UHS-1 or better. A card can either be purchased locally or from AliExpress. Be warned that there is an ongoing problem with the production and sale of fraudulent memory cards misreporting the available storage and even supplies from a reputable outlet can be affected - test the card you purchase. The AliExpress link has been used successfully to obtain suitable micro SD cards.
Raspberry Pi 4
These are likely to be available to be purchased locally or from a domestic online source. You need at least a 2GB RAM model. The Raspberry Pi Model 3B+ is the minimum specification, and a Raspberry Pi Model 4B is preferred. Purchase the official 5.1V 3A 15.3W power supply to go with it - most problems with Raspberry Pi units are due to inadequate power supplies being used instead of purchasing the official power pack. Note: to connect a RPi 4B to a monitor you will also need a micro-HDMI cable, so that might be necessary to add to the shopping cart also.
Additional items and tools
- If the camera lens does not arrive with two small screws to mount the lens to the camera, you will need to locate two suitable small screws.
- A tube of silicone sealant is used to seal the glass window for the housing and the front screws in the housing.
- Self-amalgamating tape can be used to wrap and seal the cable connector(s) to ensure they remain weathertight in all conditions.
- Tools such as small wire cutters or a sharp knife, various sized screwdrivers, a drill and screws to mount the camera bracket will be required.
Deprecated shopping list: LINK
Some cameras come with a slightly different cable with a separate 12v socket for power input as shown here. If you have this cable you will need a pair of PoE adapters (seen in that picture in the background). If your camera has a single cable as shown in the main picture, you will need a PoE injector or single adapter.
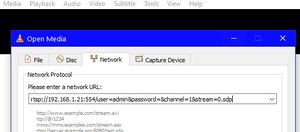
To test and focus the camera you will need VLC. This software is preinstalled on the Pi but is also available for Mac, Windows or Linux from here.
Assembly
[Note: there's a longer version of the camera assembly section of this page available on Google Docs. Please refer to this if you need more information.]
Preparing the Lens
|
Attaching the Lens to the Camera
|
Preparing the Camera Housing
|
Attaching the Camera
See image for the proper camera board orientation, so the video is not sideways or upside down. |
Installing the Camera in the Housing
|
Testing and FocusingAt this point, your camera must be tested and focused. There's no point sealing up the housing and screwing it to the wall if its not working or isn't focused ! Testing the Camera
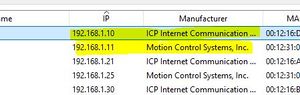
The Camera PoE cable lights should come on, indicating traffic is flowing. After a few seconds, it should steady down to irregular flashing. If you don't see flashing lights then check the cable connections to make sure everything is plugged in properly. Find its IP AddressThe camera should now appear as a device on your network and to test it properly you will need to find its IP Address. The easiest way to do this is using a free piece of software called [IP Scanner]. Download and run it (no need to install). Click "Scan" and wait till it finishes. The camera can be identified by Manufacturer 'ICP Internet Communications' or 'Motion Control Systems' (see screenshot - i have five cameras!). Checking the Connection
|
Checking for Obstructions
|
Focusing the CameraThere's a whole separate section of the Wiki on focusing, but here's the short version !!
Note that there's a short lag due to the network, so you should wait a second or two after each adjustment to allow the change to be reflected in VLC. |
Setting Camera ParametersTo operate at night, the camera must be reset to the correct gain, colour mode and video mode. There are two ways you can do this: Using the CMS SoftwareCMS is a security camera software package you can download from the internet. You can use the CMS software as explained in this video by Denis Vida. Note however that you should reset the network as the LAST thing you do. The video does it a bit soon. Using the RMS software (only for Pi4 systems)
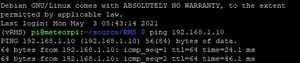
ping a.b.c.d
python Utils.SetCameraAddress a.b.c.d 192.168.42.10
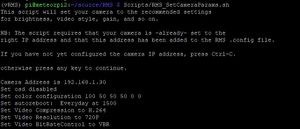
Scripts/RMS_SetCameraParams.sh
|
Final StepsSealing the HousingDepending on your climate, its usually advisable to seal up the camera housing against rain and snow. From the outside, carefully go round the edge of the glass with silicone sealant. Also squirt sealant into any screw holes visible on the front of the camera housing, where it will be most exposed to rain. But DONT seal up the hinged door because you will occasionally need to maintain the camera, and you don't want to have to prise it open with a chisel! |
Mounting OutsideMount the camera somewhere with a good view of the sky and without too many 'terrestrial' obstructions such as trees, hills and buildings. Take special care to angle well away from security lights. These lights emit infrared and without the IR Block filter, the IMX cameras are extremely sensitive to this. When locating the camera, bear in mind that you will need to be able to get to the camera to maintain it. The cameras do not need to be high up as long as they have a good view of the sky. Mine are at eye-level on my observatory shed. As before, don't worry if its not practical to eliminate all obstructions as you can mask off any that can't be avoided. Aiming the CameraThe cameras have a field of about 40-45 degrees vertically and 90 degrees horizontally so angle the camera upwards at between 35-45 degrees. This should maximise meteor detection. If you can arrange so that the camera view overlaps with other RMS users, thats even better. Check with the network to get an idea of a good direction. In this photo, the camera is aimed up at about 40 degrees, just above the top of the hill behind the camera location. The parts of the hill that are visible will be masked off in the software to avoid 'meteor-wrongs' due to dog-walkers with head torches! |
Thats it!
Once the camera is installed, connect up the PoE adapter, attach a long network cable and run it to wherever you are going to keep the Raspberry Pi. Remember to ask permission before drilling holes in the walls... :)
Now install the Software
Now you can finish configuring the Raspberry Pi by installing a prebuilt image. This is covered in a separate guide here.